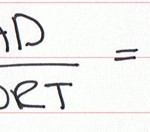I’ve always loved dragons so I’m going to have a go at making an automata of a dragon flying. I got most of my inspiration from an automata made by a guy called Keith Newstead: I love the smooth motion! I think I’ve worked out that it’s made from a crank to describe the elliptical […]